Pressure in a Fluid
Pressure in a Fluid: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Pressure Due to Fluid, Density of Fluids, Force on Side Wall of Liquid Vessel & Torque on Side Wall of Liquid Vessel etc.
Important Questions on Pressure in a Fluid
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is where is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one-fifth, the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
A U-tube having a horizontal arm of length , has a uniform cross-sectional area . It is filled with water of volume . The volume of a liquid of density required to be poured in one arm of the U-tube so that no water is left in the horizontal arm of the tube is (take )
A liquid of mass is filled in a flask, as shown in the figure. The force exerted by the flask on the liquid is
(Take, and neglect the atmospheric pressure)
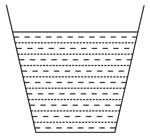
An open cubical tank was initially fully filled with water. When the tank was accelerated on a horizontal plane along one of its side it was found that one third of volume of water spilled out. The acceleration was
A bucket contains water filled upto a height= 15 cm. The bucket is tied to a rope which is passed over a frictionless light pulley and the other end of the rope is tied to a weight of mass which is half of that of the (bucket+water). The water pressure above the atmospheric pressure at the bottom is
A laminar stream is flowing vertically down from a tap of cross-section area 1 cm2. At a distance 10 below the tap, the cross-section area of the stream has reduced to 1/2 cm2. Find the volumetric flow rate of water from the tap
A vertical uniform U tube open at both ends contains mercury. Water is poured in one limb until the level of mercury is depressed 2cm in that limb. What is the length of water column when this happens.
In air an object weighs , when immersed completely in water the same object weighs . When immersed in another liquid completely, it weighs . Find The specific gravity of the other liquid
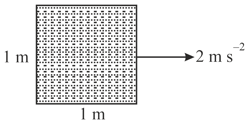
An open cubical tank completely filled with water is kept on a horizontal surface. Its acceleration is then slowly increased to as shown in the figure. The side of the tank is . Find the mass of water that would spill out of the tank.
A spherical tank of 1.2 m radius is half filled with oil of relative density 0.8. If the tank is given a horizontal acceleration of 10 m/s2. Calculate the maximum pressure on the tank ?
A piston of mass M = 3kg and radius R = 4cm has a hole into which a thin pipe of radius r = 1cm is inserted. The piston can enter a cylinder tightly and without friction, and initially it is at the bottom of the cylinder. 750gm of water is now poured into the pipe so that the piston & pipe are lifted up as shown. Find the height H of water in the cylinder h of water in the pipe
Pressure inside two soap bubbles are 1.01 and 1.02 atmospheres. Ratio between their volumes is
If the dimensions of a physical quantity "Pressure" are given by , then the physical quantity will be.
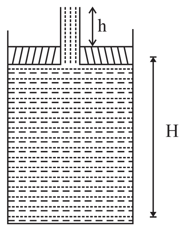
One end of a glass capillary tube with a radius is immersed into water to a depth of . The pressure required to blow an air bubble out of the lower end of the tube is _____ (surface tension and )
A wall of length supports water to a height as shown in the fig. Choose the correct statement(s)
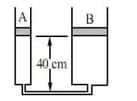
Two vertical conducting cylinders and of different cross sections are connected by a thin tube as shown. An ideal gas is trapped in the cylinders by two airtight pistons of masses and respectively. Initially the pistons are at the same height above the base of the cylinders. If an additional mass of were gently placed on the piston in the cylinder , Which of the following statements correctly describe the new steady state ultimately reached.
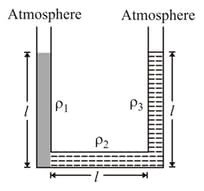
Three liquids having densities, and are filled in a U-tube. Length of each liquid column is equal to and liquids remain at rest (relative to the tube) in the position. It is impossible that:
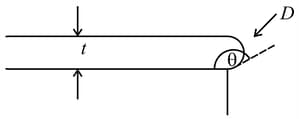
An amount of water is poured on top circular face of a horizontal glass cylinder. Excess amount of water spills over the edges and a little amount of water remains there in a thin uniform layer, a portion of which is shown in the figure. If contact angle is and surface tension of water is , the vertical thickness of the water layer far away the edge is . the point in the plane of the diagram on the liquid where the liquid protrudes the most is . The vertical depth of this point from the horizontal free surface of the water layer is . is density of water and is acceleration due to gravity. Mark the CORRECT relation(s)
A cubical container of side length '' is half filled with liquid of density and placed on the floor of an elevator accelerating downward with acceleration . Now the container is given a horizontal acceleration with respect to elevator parallel to one of the horizontal edges, and the acceleration is gradually increased in such a way that liquid in the container never start oscillation. Then, ( atmospheric pressure)
A liquid of density is filled in tube having three vertical arms each of length as shown. Initially height of liquid in each arm in 2$. If left vertical arm is closed and whole system is rotated with angular velocity about axis through middle arm, height of liquid in left arm becomes . Given
(Assume air is ideal gas and tube is perfectly conducting)